All scientific disciplines are based on mathematics, and data science is no exception. When the problems to be solved are optimization problems, you need to know what the limit of a function is. In this article, you’ll discover how to determine the limit of a function.
Limit: Definition
The limit of a function [latex]f[/latex] is the value the function approaches when its argument approaches a certain value.Mathematically, we write [latex]lim limits_{x to a} f(x) = l[/latex]
We say that [latex]f[/latex] tends towards [latex]l[/latex] when [latex]x[/latex] tends towards [latex]a[/latex].Depending on the case, [latex]a[/latex] and [latex]l[/latex] may be real numbers, or equal to [latex]pm infty[/latex].
Limits of standard functions
– Real-valued finite limits
For example, for [latex]f(x) = x^2[/latex], the limit when [latex]x[/latex] tends towards [latex]2[/latex] is [latex]2^2 = 4[/latex].
– Infinite limits
When the function is well defined at a real number [latex]a[/latex] (it is said to be continuous at [latex]a[/latex]), then the limit at [latex]a[/latex] is exactly [latex]f(a)[/latex].
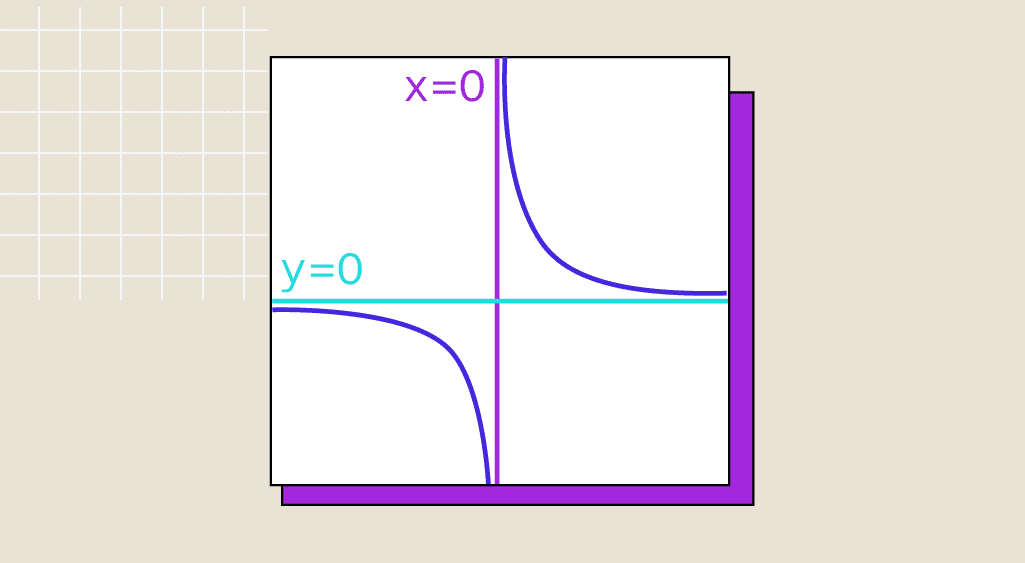
When the variable [latex]x[/latex] takes on very large values (positively or negatively), we say that [latex]x[/latex] tends towards more or less infinity. In this case, we distinguish between cases where [latex]f(x)[/latex] approaches a finite value and those where [latex]f(x)[/latex] moves away towards infinity. In the former case, [latex]f[/latex] is said to converge, and in the latter, [latex]f[/latex] to diverge.
Below is a table summarizing the limits of common functions at infinity.
[latex] In most cases, it is possible to perform limit operations to determine the limit.Limit of a sum of two functions To determine limits, it’s sometimes simpler to use other functions. Let [latex]f[/latex] and [latex]g[/latex] be two functions defined on an interval [latex]I = [a, +infty[[/latex]. Let [latex]f[/latex], [latex]g[/latex] and [latex]h[/latex] be three functions

When a function admits a finite limit [latex]l in mathbb{R}[/latex] when [latex]x to infty[/latex], then we say that [latex]f[/latex] admits a hor
begin{array}{|c|c|}
hline text{Function} & text{Limit} 0, : x to 0 \
hline f(x) = frac{1}{x} & begin{cases} & +infty text{ si } x gt 0 \ & infty text{ si } x lt 0 end{cases} \
hline nan & nan \
hline f(x) = ln(x) & -infty \
hline f(x) = sqrt{x} & 0 \
hline
end{array}
[/latex]When [latex]lim_{x to a} f(x) = pm infty[/latex], with [latex]a[/latex] a real number, then the curve of [latex]f[/latex] is said to have a vertical asymptote at [latex]a[/latex]. In other words, the curve moves closer and closer to the straight line with equation [latex]x=a[/latex].
Find out more about our Data Science training courses
Limit operations
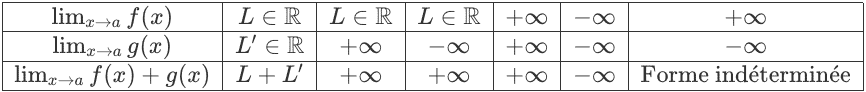
Limit of a product of two functions

Limit of a quotient of two functions

Click on the tables to display them full-screen. Determining a limit in practice
Comparing functions allows you to compare their limits, when they exist.
There are two main properties for comparing functions– Comparison theorem
Assume that for any [latex]x in I ; f(x) geq g(x)[/latex]If [latex]lim_{x to +infty}g(x) = +infty[/latex], so [latex]lim_{x to +infty}f(x) = +infty[/latex]
If [latex]lim_{x to +infty}f(x) = -infty[/latex], so [latex]lim_{x to +infty}g(x) = -infty[/latex]– Gendarme theorem
Training in Data Science